BUDGETING AND SAVING
BUDGETING
Budgeting can be defined as a tactical approach in handling one’s financial resources. It helps in monitoring one’s sources of income such as salary or business profits and organizes expenditures such as housing, food, and entertainment; this in turn helps one understand the amount of money available, how it’s being spent and what changes should be made.
The beginning of the budgeting process consists of several fundamental phases:
List Your Income: This is calculating the amount that is earned every month after taking into account tax.
Track Your Expenses: Anything and everything you spend money on during the month, record (fixed costs such as rent/mortgage, utilities and variable costs such as dining out, entertainment, etc).
Set Financial Goals: How much are you planning to save, invest, or pay off in debt every month?
Prioritize: Recognize necessary coverage while curtailing unnecessary coverage e.g. unsubscribe from channels you don’t watch or cut out frivolous purchases.
Adjust as Needed: Adjustment should be done periodically through re-examination as well as revision of the guidelines put in place.
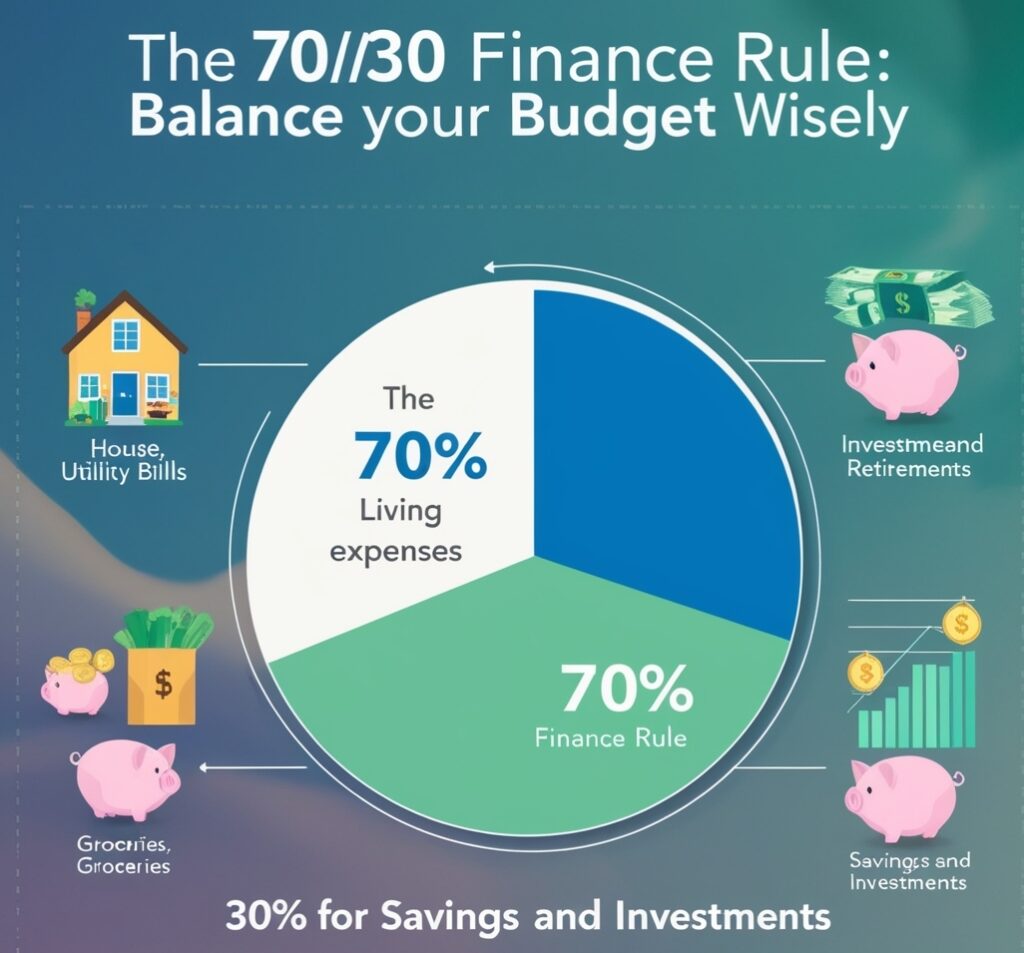
There are many other types of budgeting strategies such as the 50/30/20 rule; which states that one should not spend more than fifty percent of their income on their needs and 20% on savings and debt, the Fifty-Five categories spending plan, also know as the 55/45 budget or simply the 55/45, which divides expenses as a proportion of income earned; or the Zero-based budgeting which is allocating every dollar to a category – leaving no unallocated dollars.
SAVING
Saving can be defined as the continuous effort of excluded any certain portion of income as it goes In order to meet given financial horizons, building a reserve, and more importantly creating wealth for the long term.
Other factors in saving are:
Pay Yourself First: As said earlier set aside something that you will save however much less you think it is may be towards bill payment and other spendable resources.
Emergency Fund: This is an amount of money which can sufficiently sustain an individual for three to six months’ worth of expenses for unforeseen cases such as job loss or medical needs.
Set Specific Goals: Think of a vacation, buying a house, or retirement. Those will give you precise targets for your savings.
Automate Savings: Schedule electronic transfers to your savings account so that you do not have to rely on your will power every time.
Invest With Caution: For savings that are to be maintained for a longer period, consider investing in income-generating assets like stocks, bonds, or even retirement accounts.
A good saving strategy will help you in avoiding use of credit in instances of emergencies, alleviate anxiety in such situations and also prepare you for future needs. It also brings a positive feeling of financial stability and independence.
To sum it up, budgeting prevents you from overspending whereas saving enables you to have adequate finances in future. Both these situations form very important parts of a balanced financial life.